×
C. de Vente, A. Tufail, S. Schmitz-Valckenberg, M. Saßmannshausen, C. Hoyng and C.I. Sánchez on behalf of the MACUSTAR consortium. "OCT Super-Resolution for Data Standardization using AI: A MACUSTAR report", in: Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology, 2023.
@conference{Vent23c,
author = {de Vente, Coen and Tufail, A. and Schmitz-Valckenberg, S. and Saßmannshausen, M. and Hoyng, C. and S{\'a}nchez on behalf of the MACUSTAR consortium, Clara I},
title = {OCT Super-Resolution for Data Standardization using AI: A MACUSTAR report},
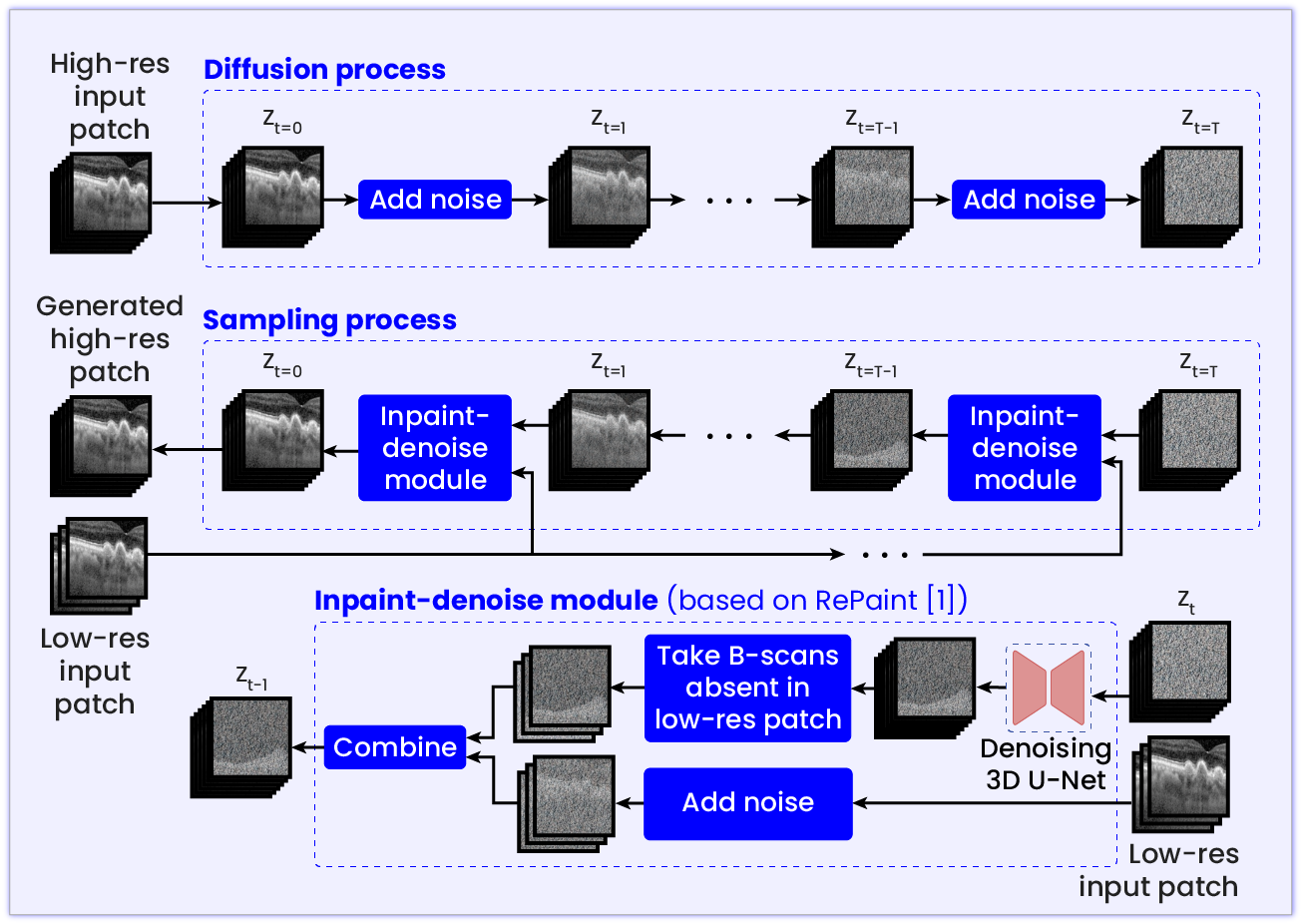
Methods: The MACUSTAR cohort, a European multicentre study, was used as a training set with 743 OCTs from 181 patients and validation set with 26 OCTs from 26 patients (n=3 no AMD, n=2 early AMD, n=18 intermediate AMD, n=3 late AMD). All scans were Heidelberg Spectralis OCTs with 241 B-scans. We trained a 3D diffusion model to generate high-resolution OCTs, which was used during evaluation to produce OCTs with 241 B-scans from OCTs with 120 B-scans. The performance was calculated using the mean squared error (MSE) on OCT volume-level between the generated B-scans and the original B-scans.
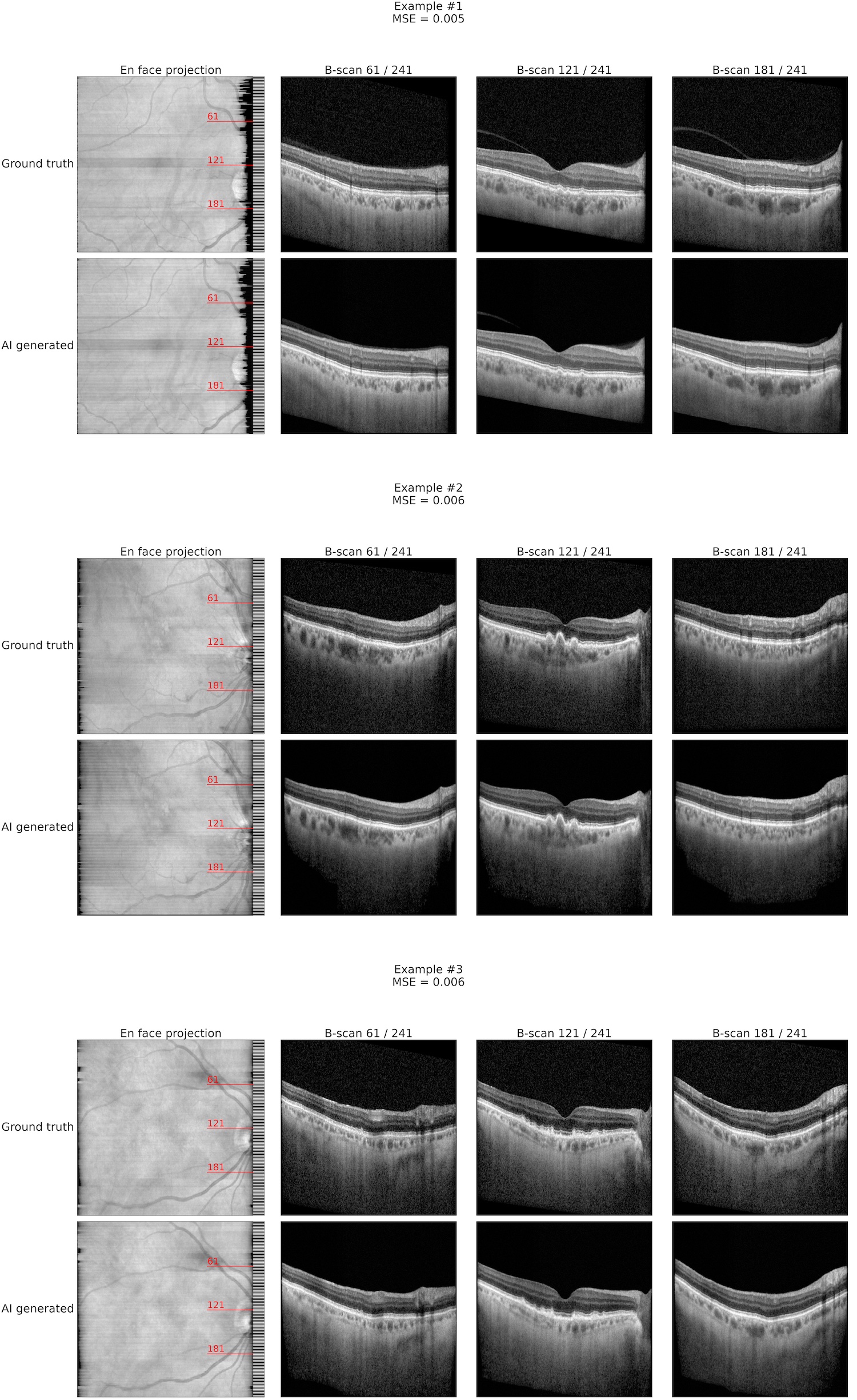
Results: The MSE between the generated B-scans from the low-resolution OCTs and the original B-scans from the high-resolution OCTs was 0.006 ± 0.004 (mean ± SD). Fig. 1 shows visual examples of the generated OCTs compared to the original B-scans in the validation set.
Conclusions: We showed the feasibility of the proposed approach to generate super-resolution OCTs, which is one of the required steps to standardize high-quality OCTs within multicenter studies. In extensions of this approach, coherence between the OCT and other modalities, such as en face imaging and other metadata, could be introduced, allowing the AI model to make better informed generative decisions.
},
year = {2023},
booktitle={Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology},
journal={Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science},
volume={64},
number={8},
pages={313--313},
publisher={The Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology},
url={https://iovs.arvojournals.org/article.aspx?articleid=2789903}
}
 26 March 2023
26 March 2023 26 March 2023
26 March 2023 Poster (PDF)
Poster (PDF)
 Copy
Copy
 LinkedIn
LinkedIn
 QurAI
QurAI
 DIAG Nijmegen
DIAG Nijmegen